The landscape of digital marketing is undergoing a seismic shift, moving from a reactive posture to one of proactive anticipation. For decades, success was defined by a brand’s ability to be present and relevant when a consumer acted.
Today, competitive advantage is increasingly determined by a brand’s ability to anticipate that action before it even occurs. This transformation is driven by the convergence of two powerful forces: a fundamental change in consumer behavior, crystallized in the concept of “micro-moments,” and the maturation of artificial intelligence (AI) as a predictive engine.
This article will deconstruct this new paradigm, exploring the technologies, strategies, and real-world applications that define success in the age of predictive marketing. We will examine the foundational concept of micro-moments, dissect the core AI technologies that power prediction, showcase how leading brands are translating these insights into impact, and look ahead to the future trends shaping this revolutionary approach.
Understanding Micro-Moments
The modern consumer journey is no longer a linear, predictable path but a fragmented series of brief, high-intent interactions. Coined by Google, these are known as “micro-moments”: fleeting, intent-rich instances when individuals reflexively turn to a device—overwhelmingly a smartphone—to act on a specific, immediate need.
These moments, often lasting just seconds, are the new battleground where brand perceptions are formed, preferences are shaped, and purchasing decisions are made.
Successful marketing strategies are built upon a universal understanding of the four foundational categories of micro-moments:
- I-want-to-know moments: This category encompasses instances of research and exploration. The consumer is curious and seeking information but is not yet in a transactional mindset. Examples include searching for product reviews, comparing features, or learning about a new topic.
- I-want-to-go moments: These are driven by local intent, where a consumer is looking for a nearby business or planning a journey to a physical location. Searches often include terms like “near me” or are implicitly localized by the search engine.
- I-want-to-do moments: This category centers on instructional needs. The consumer is seeking guidance on how to complete a task, learn a new skill, or use a product. This often leads them to how-to videos, tutorials, and step-by-step guides.
- I-want-to-buy moments: These are high-value, transactional moments when a consumer has made a decision and is ready to purchase. Their focus shifts to finding the best deal, confirming availability, and completing the transaction with minimal friction.
In these moments, consumer expectations are extraordinarily high. They demand immediate, useful, and highly relevant answers tailored to their specific context. This dynamic has led to a fundamental redefinition of brand loyalty. Evidence suggests that during these high-intent searches, consumers are more loyal to their immediate need than to any particular brand.
The brand that delivers the most valuable and frictionless experience wins the moment and, increasingly, the customer’s business.
How AI Anticipates Customer Needs
For years, the strategic advice for marketers has been to “be there” and “be useful” in these critical micro-moments. While necessary, this is no longer sufficient.
The next evolutionary leap is the shift from simply being present to actively anticipating these moments. Artificial intelligence is the game-changing technology powering this transformation, enabling a move from a reactive to a proactive marketing discipline.
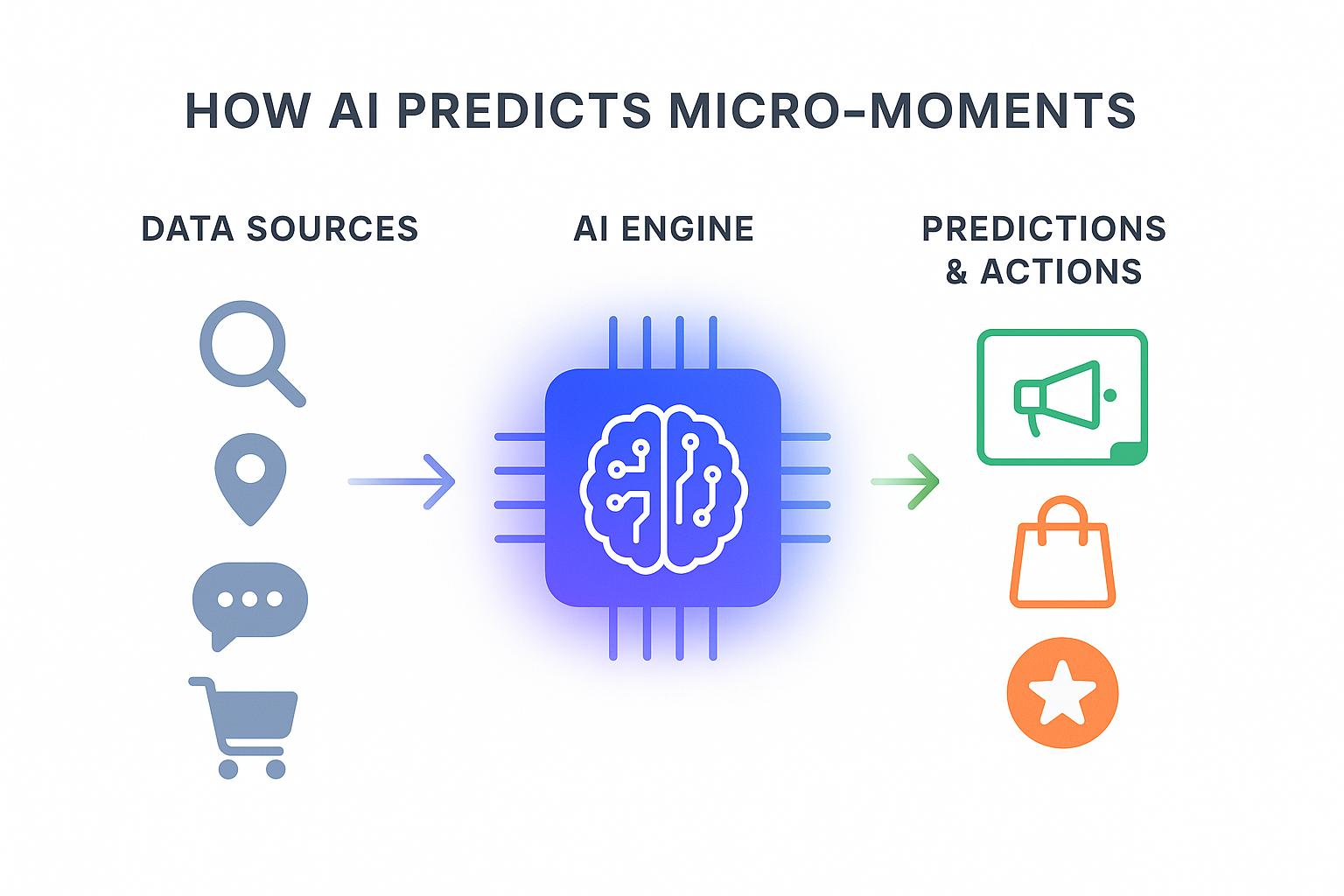
AI achieves this by analyzing vast and complex datasets to identify the subtle patterns that precede a consumer’s need. Understanding how this predictive engine functions requires a look at its core components:
Machine Learning (ML): The Pattern-Recognition Powerhouse
At its core, ML builds systems that learn from data to identify patterns and make decisions. In this context, ML algorithms sift through immense datasets, including historical purchases, real-time clickstream data, and app usage, to uncover the hidden behavioral signals that precede a specific micro-moment.
For example, an ML model can learn that users who exhibit a specific sequence of clicks have a high probability of entering an “I-want-to-buy” moment, allowing a brand to intervene with a timely offer.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Deciphering Human Intent
A vast amount of customer intent is expressed through unstructured language in search queries, social media comments, and product reviews. NLP is the field of AI that gives computers the ability to read, understand, and derive meaning from this language. Using techniques like word embeddings, NLP can distinguish between the search query “running shoe reviews” (an “I-want-to-know” moment) and “buy running shoes” (an “I-want-to-buy” moment), allowing for a far more nuanced response.
Predictive Analytics: From Patterns to Prophecies
Predictive analytics is the framework that operationalizes the insights from ML and NLP. It uses statistical models to analyze current and historical data to make predictions about future events. As defined by Gartner, this discipline emphasizes prediction over simple description. A predictive model might output a “propensity score” for a customer, quantifying the likelihood they will make a purchase or churn, allowing brands to anticipate and shape future outcomes rather than just analyzing what has already happened.
Strategic Applications of Predictive AI
The true value of a predictive engine lies in its ability to drive tangible business outcomes. By translating predictive insights into strategic actions, organizations can create superior customer experiences and generate measurable growth.
Hyper-Personalization at Scale
This is the most prominent application of predictive AI. It moves beyond basic personalization (like using a first name in an email) to the practice of using real-time data to deliver dynamically tailored content, product recommendations, and offers based on a user’s predicted intent.
AI makes this possible for millions of individuals simultaneously, allowing a brand’s website content to shift dynamically as a user clicks and for personalized email offers to be triggered by in-session behavior. The goal is to create marketing that feels uniquely handcrafted and helpful to the individual.
Predictive Customer Journey Mapping
The traditional marketing funnel is an inadequate model for the modern, non-linear consumer journey. AI-powered predictive analytics allows businesses to map, understand, and influence this complex journey in real time. Instead of relying on static maps, AI models can predict a user’s “next best action” and identify which users are likely to convert or churn. This enables proactive interventions, such as automatically triggering a loyalty offer if a user’s behavior matches the patterns of previous customers who churned.
Real-Time Responsiveness
Speed is critical in micro-moments. Consumers expect instant gratification, and research shows that even a one-second delay in mobile page load time can negatively impact conversion rates. AI is the enabling technology that allows brands to operate with the immediacy these moments demand. This includes dynamically adjusting ad placements, automating content delivery, and personalizing website experiences on the fly, which is no longer a luxury but a baseline expectation.
Navigating the Future of Predictive Marketing
The technological and strategic landscape continues to evolve at an accelerated pace. The future will be shaped by new technologies, inherent challenges, and critical ethical considerations.
The Next Disruption: Generative AI & the “Zero-Click” Search
The emergence of powerful generative AI models integrated directly into search engines represents a significant disruption. According to a report from Forrester Research, tools like Google’s AI Overviews and ChatGPT are ushering in a “zero-click” search era. In this new paradigm, users receive direct, synthesized answers to their queries within the AI summary, often eliminating the need to click through to a company’s website.
This shift necessitates an evolution from Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to “Generative Engine Optimization,” where the goal is to become the authoritative source the AI model cites in its response. In a very real sense, marketers must now market to the AI.
Challenges & Ethical Lines
The implementation of predictive AI is not without hurdles. The accuracy of any prediction is entirely dependent on the quality of the underlying data; “garbage in, garbage out” is paramount. Furthermore, AI models trained on historical data can learn and amplify existing biases, creating significant brand and legal risk.
Beyond the technical challenges lies the most critical long-term consideration: navigating the fine line between helpful personalization and intrusive surveillance. Hyper-personalization without transparency is perceived as surveillance, and consumers are increasingly sensitive to it. Building and maintaining customer trust through ethical data practices must be the guiding principle.
Winning the Moment
The imperative to adopt predictive strategies is driven by undeniable trends in consumer behavior.
Attention spans have contracted, while expectations for speed and relevance have soared. In this environment, mastering the prediction and fulfillment of micro-moments is not just a path to optimization but a prerequisite for survival and growth.
The brands that will lead the future are those that blend AI’s intelligence with a deep, empathetic understanding of the human needs driving every interaction. They will be fast enough to be relevant, smart enough to be personal, and human enough to be trusted.